If you’ve ever marveled at lightweight yet incredibly strong materials used in boats, cars, or electronics, chances are you’ve encountered fiberglass. Understanding fiberglass can open doors to smarter material choices for your projects, whether you’re building a structure, crafting a vehicle, or designing high-tech electronics. In this guide, you’ll discover what fiberglass is, how it’s made, its types, key properties, and why it might just be the perfect material for your next endeavor.
What Is Fiberglass?
![What-is-fiberglass]()
In simple terms, fiberglass is a composite material made from extremely thin fiberglass. Think of it as a combination of glass threads to create a lightweight, durable, multifunctional fabric.
These fibers are usually combined with resins to form strong, rigid materials used across countless industries.
In essence, fiberglass gives you the strength of glass without the fragility, and the flexibility to use it in ways you might not have thought possible.
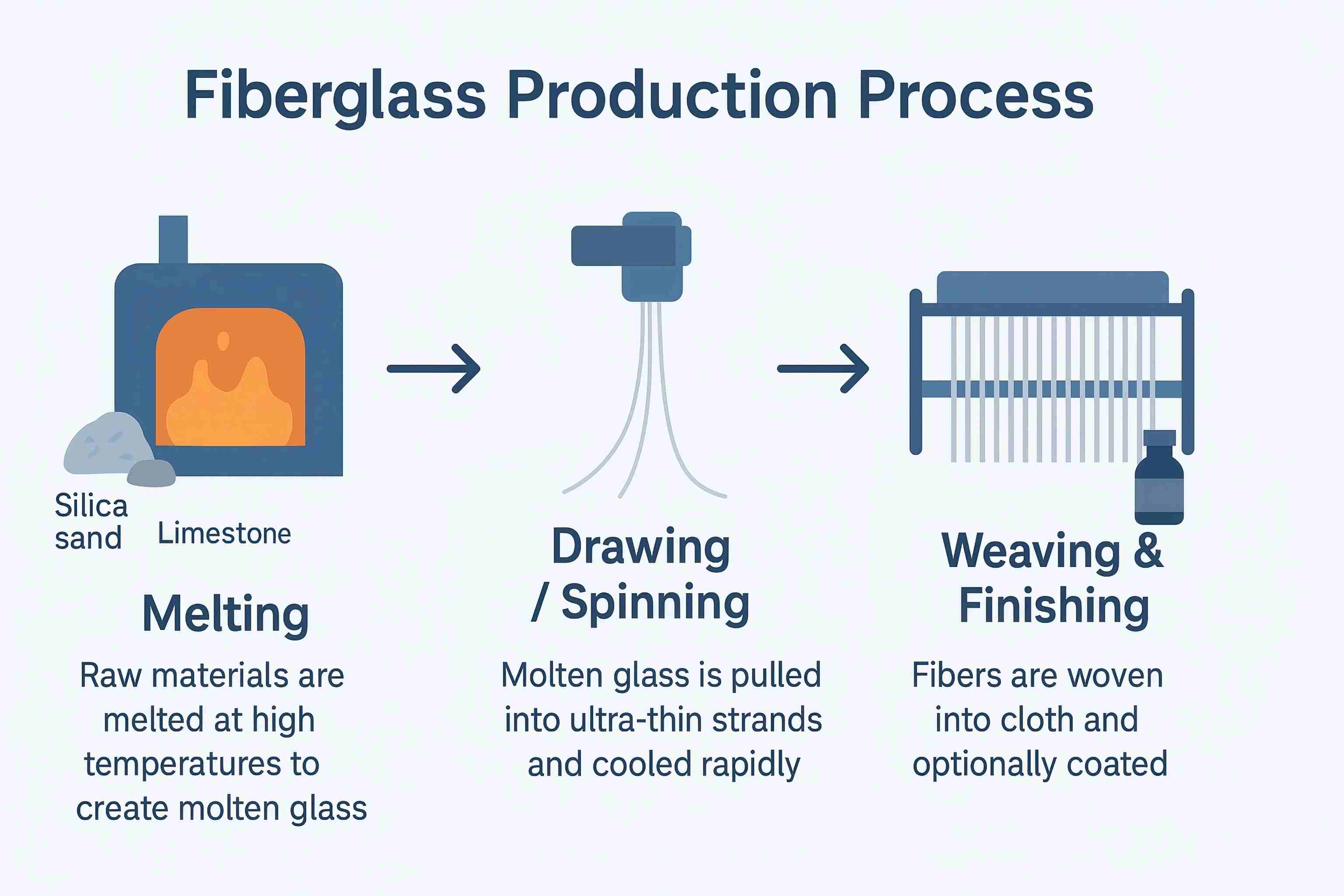
How Fiberglass Is Made
The production of fiberglass involves three key steps:
Melting – Melt silica sand, limestone and other minerals at high temperatures to form molten glass.
Drawing or Spinning – This molten glass is then pulled into ultra-thin strands, often thinner than a human hair. These fibers are cooled quickly to retain their strength.
Weaving & Finishing – The fibers are woven into cloth or mats, and sometimes treated with special coatings, such as silane, to improve bonding with resins or enhance durability.
Through this process, you end up with a material that is strong, lightweight, and ready to be customized for your projects.
![How Fiberglass Is Made]()
Types of Fiberglass
Fiberglass comes in several types, each designed for specific performance needs. Here’s how you can choose the right one for your project:
E-Glass (Electrical Grade)
This is the most common fiberglass you’ll find. It’s excellent for electrical insulation, making it perfect for circuit boards, electronic housings, and other components where safety and reliability matter. You can rely on E-glass for projects where strength and moderate heat resistance are required without breaking the bank. Typical properties include a tensile strength of ~3.4 GPa and elastic modulus of ~72 GPa, with heat resistance up to 550°C.
C-Glass (Chemical Resistant)
If your project involves exposure to acids, alkalis, or harsh chemicals, C-glass is your friend. You might use it in industrial tanks, pipes, or chemical-resistant coatings. It can withstand environments with pH 1–13 and maintains structural integrity where metals would corrode quickly.
S-Glass (Structural & Aerospace)
S-glass is built for maximum strength and heat resistance. Think high-performance vehicles, aircraft components, or advanced sporting goods like racing boat hulls. When you need fiberglass that can endure extreme stress, S-glass is your go-to. Its tensile strength reaches 4.5–5 GPa, and it can tolerate heat up to 870°C.
Silane-Treated Cloth
This isn’t a “type” in the traditional sense, but a treated form of fiberglass that bonds better with resins. You’ll find it indispensable for composite materials used in aerospace, automotive, and wind energy applications, where durability and strength are critical. Using silane-treated cloth can improve composite tensile strength by 10–20% compared to untreated fiberglass.
Tip for you: Choosing the right type isn’t just about performance—it’s about efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Using E-glass where S-glass is needed can risk failure, and vice versa.
![Types of Fiberglass]()
Key Properties
Understanding fiberglass’s properties helps you make smarter material choices:
1.High Strength
Fiberglass can handle significant tension and compression. For example, panels made from E-glass reinforced composites can support hundreds of kilograms per square meter without deformation. Compared to typical plastics, it is 2–3 times stronger.
2.Lightweight
It’s lighter than steel or aluminum. Fiberglass structures are roughly 1/3 the weight of steel and 25% lighter than aluminum, helping you build large structures or vehicles that improve fuel efficiency and are easier to install.
3.Heat & Fire Resistance
Fiberglass maintains its shape and strength at high temperatures. E-glass can withstand up to 550°C, while S-glass handles up to 870°C, making it safe for oven interiors, electronics near heat sources, or automotive engine components.
4.Corrosion Resistant
Unlike metal, fiberglass doesn’t rust. You can deploy it in coastal areas, chemical plants, or outdoor structures without worrying about environmental degradation.
5.Electrical Insulation
Perfect for electronics, PCB substrates, or insulation components. Electronic-grade fiberglass cloth offers dielectric strength of 15–25 kV/mm, keeping your devices safe under electrical load.
Practical advice Think of fiberglass as a material that combines multiple benefits—strength, durability, and insulation—so you don’t have to compromise like you might with metal or plastic.
Applications You Can Explore
Fiberglass’s versatility lets you innovate in many fields:
![Construction]()
You can use fiberglass to reinforce concrete, or craft durable elements. Panels 3–5 mm thick can support hundreds of kilograms, while reducing overall structural weight by 20–30%.
![Marine & Boats]()
Fiberglass hulls and decks resist corrosion from saltwater and weather, allowing your boat to stay strong and reliable for years. Fiberglass lets you design custom shapes impossible.
![Automotive]()
Fiberglass lets you design lightweight car panels, custom bodywork, or structural parts. Substituting steel with fiberglass can reduce component weight by 15–20%, improving fuel efficiency.
![Electronics]()
With electronic-grade fiberglass cloth, you can make PCB substrates, insulation layers, or housings that endure high temperatures and electrical stress. Your devices will be safer, more durable, and reliable.
![Wind Energy]()
Turbine blades require materials that are lightweight, strong, Fiberglass composites allow blades 50–70 meters long to withstand wind speeds up to 70 m/s, ensuring efficient and long-lasting energy.
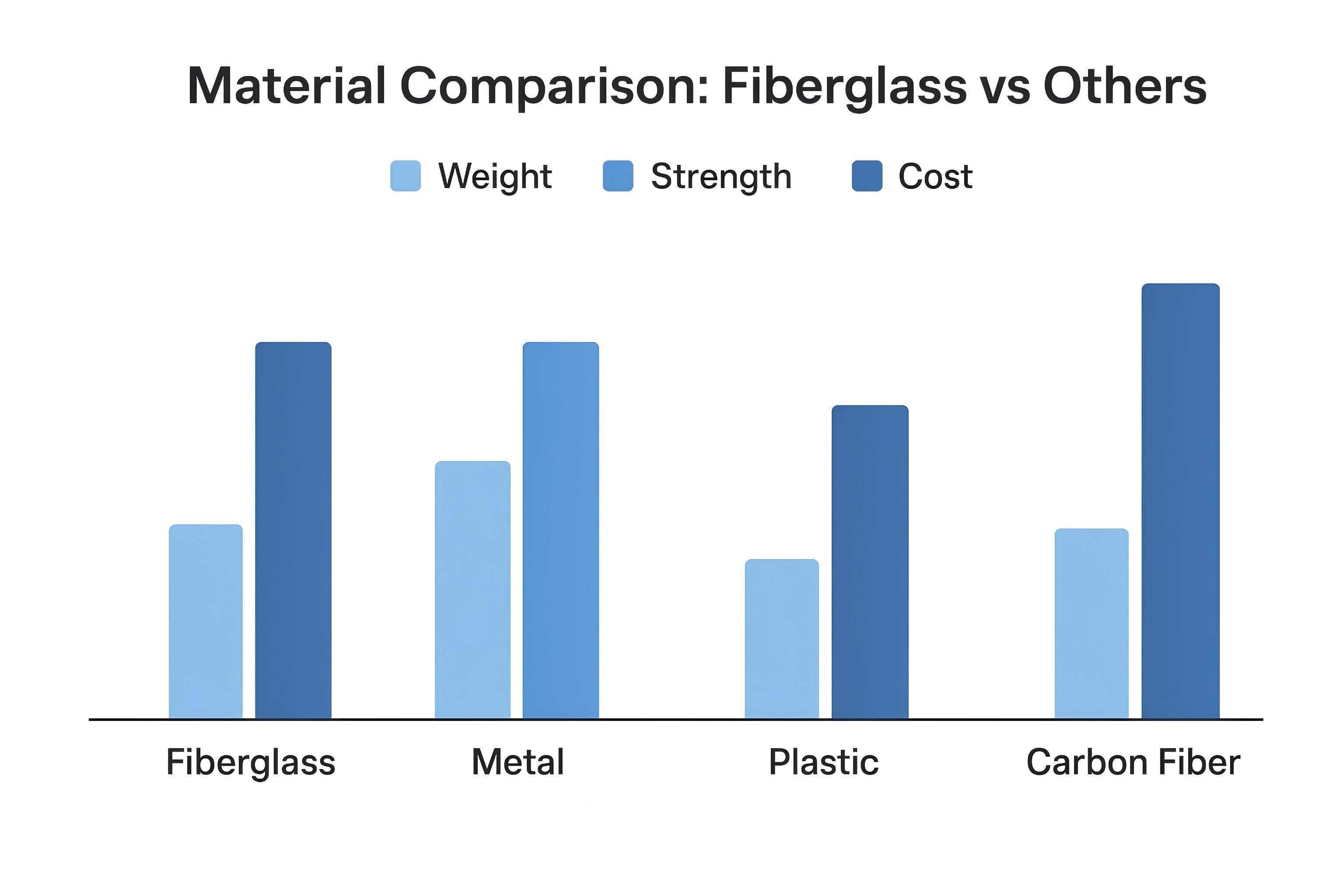
Why You Should Choose Fiberglass
Here’s why fiberglass might be better than other materials for your project:
Material | Advantages of Fiberglass Compared to It |
Metal | Lighter (~1/3 weight of steel), corrosion-resistant, easier to mold into complex shapes |
Plastic | Stronger (2–3×), more heat-resistant (up to 550–870°C), longer-lasting |
Carbon Fiber | More cost-effective ($2–5/kg vs $20–50/kg for carbon fiber) while still offering excellent strength-to-weight ratio |
Practical takeaway for you: You get the benefits of multiple materials in one. Fiberglass is strong, versatile, lightweight, and affordable—a rare combination.
![Why You Should Choose Fiberglass]()
Sustainability & Future Trends
Fiberglass is evolving to meet your environmental concerns:
1.Recyclability – Modern processes allow fiberglass composites to be recycled or repurposed, recovering ~90% of material for lower-strength applications.
2.Bio-Based Resins – Some manufacturers now combine fiberglass with plant-based resins, creating greener composites and reducing reliance on petroleum-based resins.
3.Longeity – Fiberglass structures can last 30–50 years, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
4.Future Applications – Think electric vehicles, renewable energy, lightweight drones, and sustainable construction. Using fiberglass components can cut fuel consumption and carbon emissions by 15–20% compared to heavier alternatives.
For you: Choosing fiberglass isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a forward-looking, sustainable choice.
Conclusion
By now, you’ve seen how fiberglass combines strength, lightness, and versatility like no other material. Whether you’re developing new products, optimizing structures, or looking for sustainable solutions, fiberglass gives you the freedom to innovate without compromise.
At Jlon, we’re dedicated to helping you make the most of fiberglass technology — from electronic-grade fiberglass cloth to custom composite materials tailored to your specific needs. With years of expertise and strict quality control, Jlon ensures every roll of fiberglass meets the performance standards your projects demand.
If you’re ready to explore smarter, stronger, and more sustainable material solutions, Jlon Fiberglass is here to support your vision — from concept to creation.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
Bahasa Melayu
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Dansk
اردو
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Беларуская мова
Български
ქართული
Kurdî
Кыргызча