Technical data Sheet of Chopped Strand
 TDS Chopped Stands for PP PA.pdf
TDS Chopped Stands for PP PA.pdf
Introduction of Chopped Strand
E-glass chopped strands are used as reinforcements in thermoplastics and thermoset to produce molded parts for electrical, mechanical and chemical resistant applications in transportation, construction industries, etc.
Video of Chopped Strand
Specification of Chopped Strand
Product Code | Diameter µ | Size Content % | Water Content % | Chopped Length mm | Application
|
ECS-03B | 13 | 1.6±0.2 | <0.15 | 3 | Bulking Molding Compound |
ECS-06B | 13 | 1.2±0.2 | <0.15 | 6 |
ECS-12B | 13 | 1.2±0.2 | <0.15 | 12 |
ECS-24B | 13 | 1.2±0.2 | <0.15 | 24 |
Product Code | Diameter µ | Size Content % | Water Content % | Chopped Length mm | Application
|
ECS-03P | 11/13 | 1.4±0.2 | <0.10 | 3 | Thermoplastics PA/PET |
ECS-045P | 11/13 | 1.4±0.2 | <0.10 | 4.5 |
ECS-06P | 11/13 | 1.4±0.2 | <0.10 | 6 |
Features of Chopped Strand
Uniform appearance , low static and good flowability.
Minimal glass bonding with resins, excellent surface appearance.
Good mechanical properties.
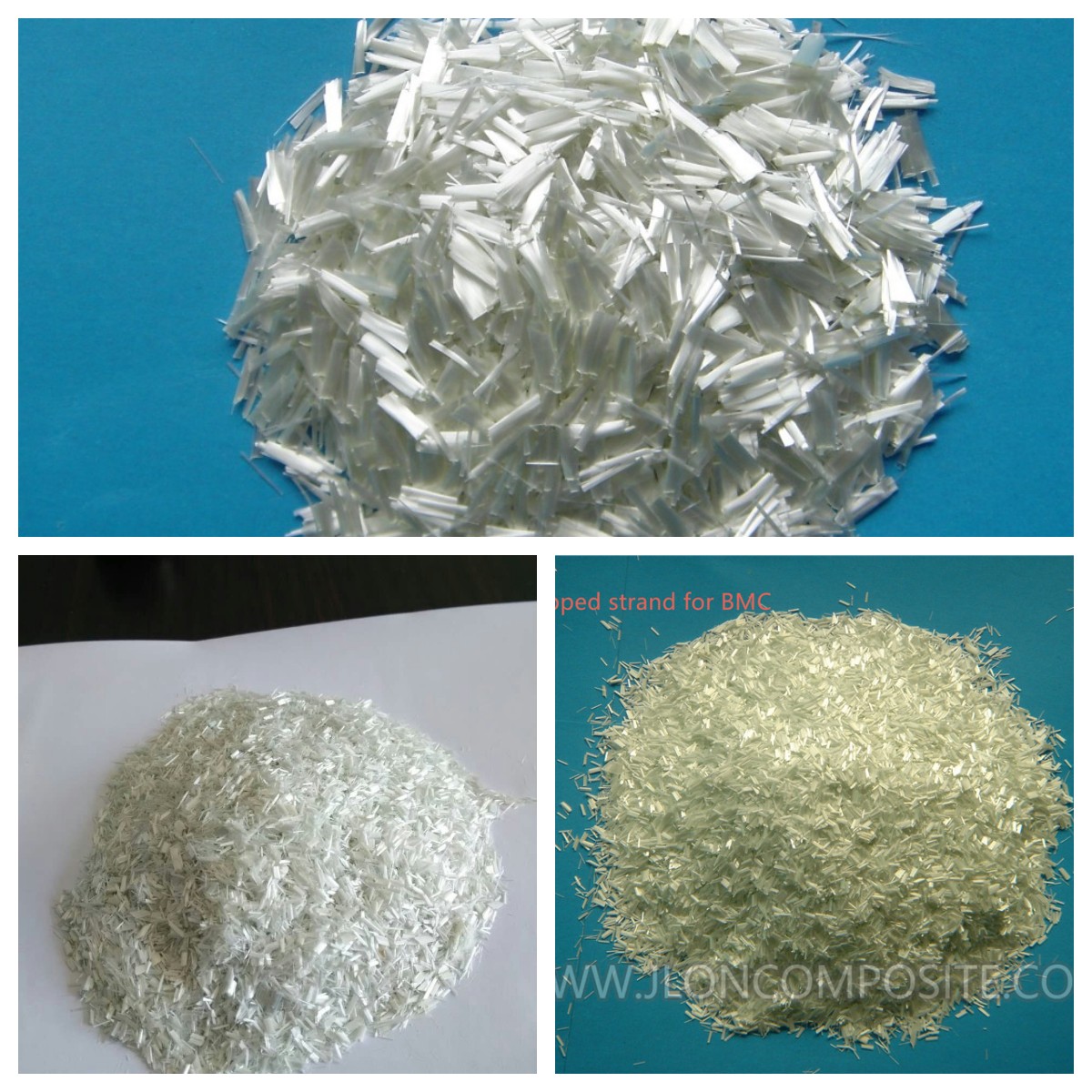

Typical Uses of Chopped Strand
Chopped strand are often added to resin systems to increase strength as well as aid adhesion. Often used for filling large voids. May be used in conjunction with Cab-O-Sil and Glass Microspheres.
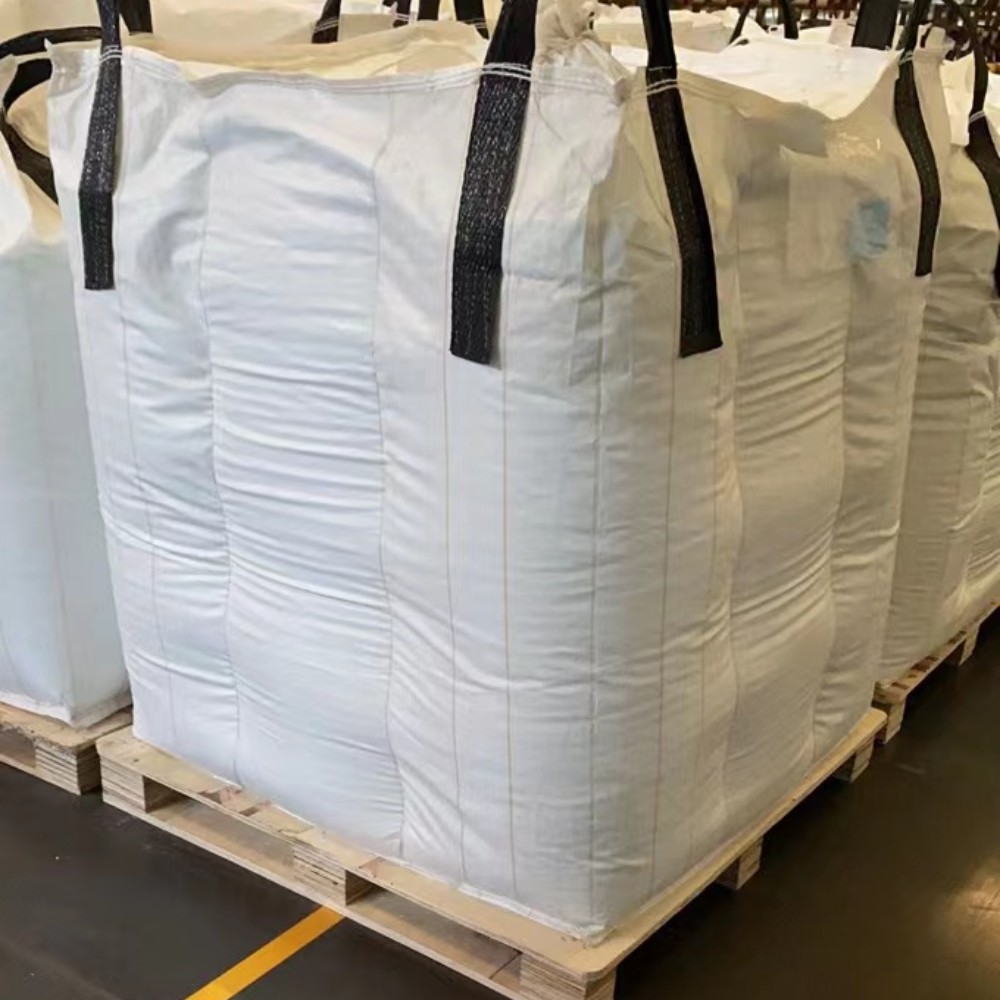
Package of Chopped Strand
Bulk bags, heavy-duty box, and composite plastic woven bags.
Bulk bags can hold 900kg-1000kg each;
Cardboard boxes and composite plastic woven bags can hold 15kg-25kg each.

FAQs of Chopped Strand
Q1.Can your company customize products?
A: Yes, We usually discuss with customers and help them find solutions.
Q2. How can I get a sample from you to check quality?
A: Usually a sample will be prepared within one week after specification agreed.
Q3. What about your delivery time? Can we receive our goods on time?
A: Usually around 2-3 weeks after order confirmed. Exact delivery time depends on order quantity and Off-season/ busy season.
Q4. What is the Guarantee to buy your products? How to resolve quality complaints?
A: Offer TDS of each lot of production for confirmation before delivery.Once you have any quality problem, you can provide samples /pictures /test data. With our quality tracking system, we will give you feedback in short time. If the quality problem confirmed,we will send you replacement or make refund as you like.
Q5. What are your terms of payment?
A: Usually we do EXW, FOB, CIF, and DDU.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
Bahasa Melayu
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Dansk
اردو
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Беларуская мова
Български
ქართული
Kurdî
Кыргызча








































































